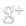It is no secret that the most frequently used programs on a computer/laptop are different browsers. Through them, the user has access to the Internet, receives, distributes, and sends information to other users. Therefore, viruses have appeared that only target browsers, without affecting other programs. Antivirus programs often do not detect such viruses; meanwhile, the user gets a lot of advertising because of them, pop-up banners, redirects to other sites, and besides the operating system slows down. These and other problems associated with browser viruses can be fixed by clearing Google Chrome, Safari, Mozilla, Edge, IE and other browsers. Let’s take a look at what a virus is in browsers, how to remove malware safely and effectively.
Is there a virus in the browser, how does the infection occur?
To begin with such an article, it is logical to cite the symptoms of a browser infection with malware (browser hijacker, pop-ups, advertising modules, adware, etc.).
The most common symptoms of a browser infection:
- Advertising banners, teasers, a link with a proposal to buy something, sell, etc. Moreover, such advertising can appear even on those sites on which it has never happened before.
- The appearance of various windows with a warning that in a few days you will be blocked; about the need to check and install a new flash player, the appearance of erotic pictures and videos, etc.
- Opening arbitrary tabs and windows in the browser. Sometimes, such tabs open after a certain period of time and not noticeable to the user. You will see this tab when you close or minimize the main browser window.
How malware gets on computers?
The most common infection of the browser by a virus occurs through the user’s fault. Usually, many users do not even pay attention to which sites they sometimes go to, which programs they install (and which checkboxes they agree with).
- Installation of programs through the “installers” and “rocking” …
The most common reason for the appearance of malware on a computer is the installation of programs through a small installer (an exe file of no more than 1 MB in size). Usually, such a file can be downloaded on various sites with software (most often on little-known torrents). When you run such a file, you are offered to start or download the file of the program itself. By the way, if you pay attention to the installation process – then in most cases you can avoid installing malware.
- Installing programs with malware
Also, malware may be “bundled” in other software. When installing such programs, you should opt out of various browser add-ons that they offer to install. The main thing – do not press the button further, without familiarizing with the installation parameters.
- Visiting erotic sites, phishing sites, etc.
There is nothing special to comment on. I recommend still not to go over all sorts of dubious links (for example, coming in a letter to the mail from strangers, or in the social networks).
- Lack of antivirus and Windows updates
Antivirus is not 100% protection against all threats, but it still protects against most of it (with regular database updates). In addition, if you update regularly and the Windows OS itself, then you will protect yourself against most of the “problems”.
Ways to remove malware
If you “caught” a virus in your browser, how to remove it? In many ways, your actions depend on the specific virus that entered the browser. However, there are universal methods that help in such situations.
Automatic removal
This is the most convenient method of removing which is suitable for users who want to get rid of the virus as soon as possible. It is also convenient because there is no need for any special knowledge since modern programs are very easy to use.
Solution for Windows users: Performing an antimalware scan with Norton would automatically search out and delete all elements related to malware. It is not only the easiest way to eliminate malware, but also the safest and most assuring one.
Solution for Mac users: Norton Antivirus is a well-established tool for Mac users that can clear your computer from malware like malware and all related files from your computer. Another important advantage of the program is an up-to-date database of computer threats which is perfect to protect your computer in case of a new malware attack.
Steps of malware manual removal
The malware is often installed in the form of an application. For example, the Webalta search engine installed applications on Windows at one time, and to get rid of it, it was enough to remove this application.
How to remove malware from Windows XP
- Click the Start button and open Control Panel
- Go to Add or Remove Programs
- Find the application related to malware and click Uninstall
How to remove malware from Windows 7/Vista
- Click the Start button and open Control Panel
- Go to Uninstall Program
- Find the application related to malware and click Uninstall
How to remove malware from Windows 8/8.1
- Right-click the menu icon in left bottom corner
- Choose Control Panel
- Select the Uninstall Program line
- Uninstall the application related to malware
How to remove malware from Windows 10
- Press Win+X to open Windows Power menu
- Click Control Panel
- Choose Uninstall a Program
- Select the application related to malware and remove it
 If you experience problems with removing malware from Control Panel: there is no such title on the list, or you receive an error preventing you from deleting the application, see the article dedicated to this issue.
If you experience problems with removing malware from Control Panel: there is no such title on the list, or you receive an error preventing you from deleting the application, see the article dedicated to this issue.
Read what to do if program won’t uninstall from Control Panel
Remove malware from browsers
How to unlock Windows Group Policies
Before you will started to remove malware from browser you should perform following instructions in Command Prompt
This step is necessary to delete Windows Group Policies created by malware
- Start Command Prompt as Administrator
- To do this in Windows 10/8 or Windows 7 click Start and in the search box type cmd. Right-click on the found result and choose Run as Administrator.
- While in command prompt type:
rd /S /Q "%WinDir%\System32\GroupPolicyUsers" - Press Enter button.
- Then type:
rd /S /Q "%WinDir%\System32\GroupPolicy" - Press Enter button.
- Finally, type:
gpupdate /force - Press Enter button.
Since some of the hijacker threats use a disguise of a browser add-on, you will need to check the list of extensions/add-ons in your browser.
How to remove malware from Google Chrome
- Start Google Chrome
- Click on More tools, then go to the Extensions
- Delete malware or other extensions that look suspicious and you don’t remember installing them
How to remove malware from Internet Explorer
- Launch Internet Explorer
- Click on the Tools/Gear icon, then select Manage Add-ons
- Delete malware or other extensions that look suspicious and you don’t remember installing them
How to remove malware from Mozilla Firefox
- Start Mozilla Firefox
- Click on the right-upper corner button
- Click Add-ons, then go to Extensions
- Delete malware or other extensions that look suspicious and you don’t remember installing them
How to remove malware from Microsoft Edge
- Start Microsoft Edge
- Click the three-dot button in the upper right corner
- Choose Extensions
- Click the gear icon near malware or other extensions that look suspicious and you don’t remember installing them
- Choose Remove
Reset your browsers
How to reset settings in Google Chrome
- Click on the icon in the right-upper corner
- Choose Settings
- Click Advanced settings
- Click the Reset button
- In “reset” window click the Reset button
How to reset settings in Mozilla Firefox
- Click the icon in the upper right corner
- Choose Help
- Select Troubleshooting Information
- Click the Refresh Firefox… button
How to reset settings in Internet Explorer
- Click on the Tools button
- Go to Internet options
- Go to the Advanced tab
- Click Reset
How to reset settings in Microsoft Edge
- Start Microsoft Edge
- Click the three-dot button in the upper right corner
- Choose Settings
- Under the Clear browsing data category select Choose what to clear
- Select everything and click Clear
Checking “hosts” file
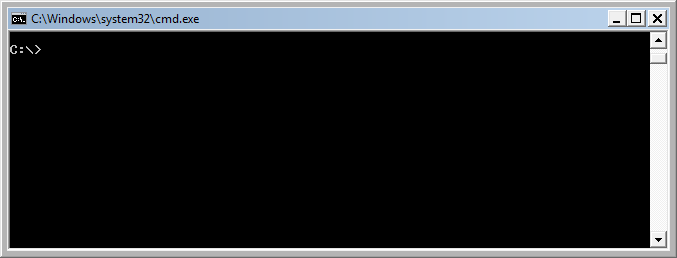
Some viruses replace “hosts” file, writing in its version of the file strings that change your connection to the sites. As a result, when opening a popular site, you get to the scam site, made by analogy. This deceptive technique is called “phishing”. Cybercriminals use it to steal your personal data like passwords, bank information and so on.
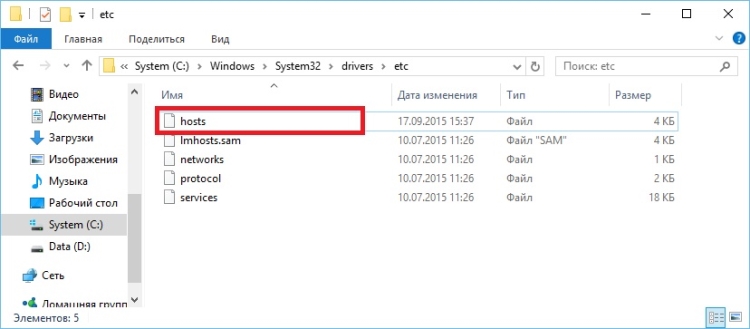
- Go to C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
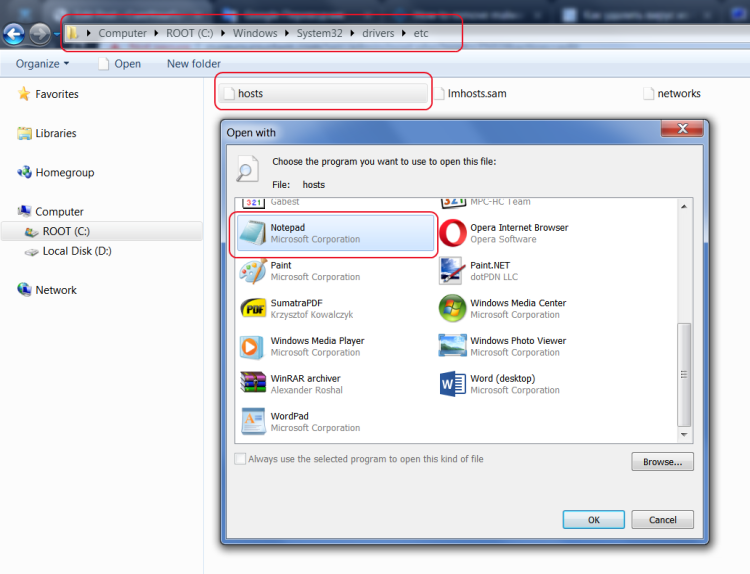
- Select and open “hosts” file via Notepad.
- Delete all entries below line 127.0.0.1. Be sure to scroll the entire file down to make sure that nothing is written below this line.
- Save and close file
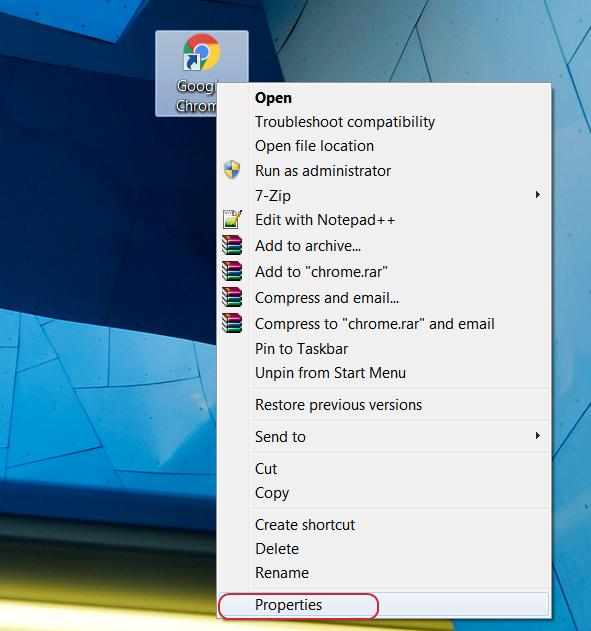
Check browser shortcuts
If your browser goes to suspicious sites after you launch it, and the antiviruses “say” that everything is ok – perhaps a malicious command was added to the browser shortcut. To check the shortcut, go to its properties (the screenshot below shows the google chrome browser shortcut).
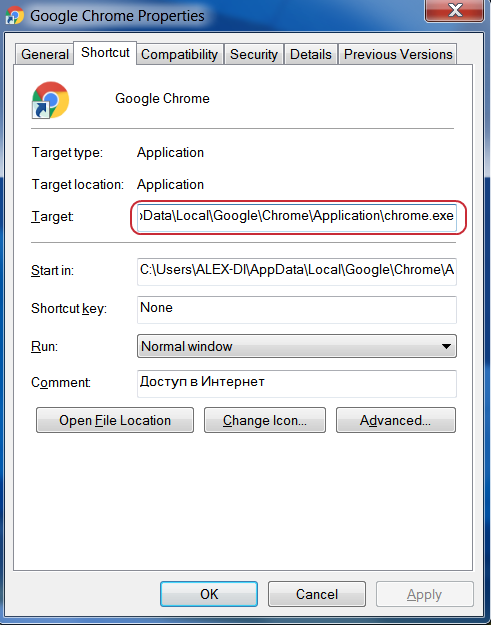
Next, look at the full launch line – “Target” or “Object”. The screenshot below shows the line as it should look if everything is ok.
Clean the Windows registry from viruses
Cleaning the registry must be done in normal (not safe) mode. To get started, go to the registry editor:
- Press Win + R, enter Regedit and press Enter.
- Viruses and unwanted programs create entries in the registry to download or update their files when Windows loads. These entries are located in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE and HKEY_CURRENT_USER registry keys along the path /Software/Microsoft/Windows/Current Version in the Run and RunOnce folders. If these branches (Run and RunOnce) have registry entries that are responsible for malicious processes, delete them. To do this, right-click on the desired file and click Delete.
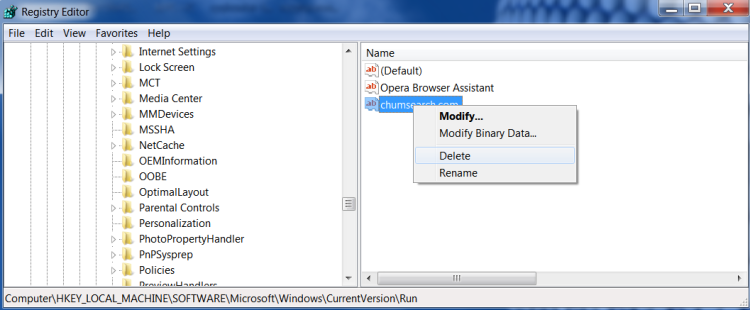
- After that, search for the names of malicious processes in the registry. In the Registry Editor, select Computer, and on the Edit tab, click Find. Enter the names of the malicious processes that you recorded and click on Find Next. Delete all found registry entries in which these processes occur. To do this, right-click on the file and click Delete. After each deletion, press the F3 key (re-search for malicious registry entries with the specified name). This action should be repeated until the registry editor detects any malicious entries for your search query. Be very careful, if you delete the system branch in the registry editor, the computer will stop working. After deleting all entries, close the registry editor.
If the above-mentioned methods didn’t help in eliminating the threat, then it’s better to rely on an automatic way of deleting malware.
We also recommend to download and use Norton to scan the system after malware removal to make sure that it is completely gone. The antimalware application will detect any vicious components left among system files and registry entries that can recover malware.