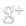There is no need to explain why you may need to remove a program – you may find it of no avail or stopped using it, or you need to free some space. And for performing this task many users rely on the most straightforward solution – they go to Control Panel. And that’s a good point since for most cases it works. But what to do if the program won’t uninstall, if it is not on the list or if you receive an error during the removal? This article might help you in solving the problem – we present here methods on how to force uninstallation of stubborn programs.
Method 1
The problem of inability to remove program is common in cases of illegitimate software. Since these programs aim to stay on the system as long as possible, the developers design the application so that it wouldn’t appear in the list of installed programs. It will do anything possible to hide its files for not to be deleted manually. Moreover, if the removal wasn’t complete, the remnants of the malware may cause repetitive installations. In this situation using an anti-malware program is the best solution.
Performing an antimalware scan with Norton would automatically search out and delete all elements related to malware. It is not only the easiest way to eliminate harmful programs, but also the safest and most assuring one.
Method 2
If the program won’t uninstall from Control Panel then you have no other choice but to remove it manually. For this, the first thing you should do is to make sure that you can access hidden files and folders.
For Windows XP
- In the Start menu click My Computer
- Choose Tools, then go to Folder Options
- Click the View tab
- Go to the Advanced Settings and check Show hidden files and folders
For Windows Vista/7
- Open Control Panel
- Choose Appearance and Personalization
- Select Folder Options
- Go to the View tab
- Go to the Advanced Settings and check Show hidden files and folders
For Windows 8/8.1
- Go to the Control Panel
- In the search bar input ‘folder’
- Click the Show hidden files and folders line
- Go to the View tab
- In the Advanced Settings category, choose Show hidden files and folders
- Click OK
For Windows 10
- Go to the Control Panel
- In the search bar input ‘folder’
- Click the Show hidden files and folders line
- Go to the View tab
- In the Advanced Settings category, choose Show hidden files and folders
- Click OK
Now you need to find the components of the program and remove them. For this, you may initiate the search on local drives and in Windows Registry Editor (to launch press Win+R, then type ‘regedit’ and hit Enter).
Method 3
Sometimes program won’t uninstall when its process is running in the background. For stopping all side processes it’s better to use Safe mode. To reboot into the Safe mode do the following:
For Windows XP:
- Restart the computer
- While the system is loading, press the F8 button several times
- Using the arrow keys choose Safe Mode and hit Enter
For Windows Vista/7:
- Restart the computer
- While the system is loading, press the F8 button several times
- Using the arrow keys choose Safe Mode and hit Enter
For Windows 8/8.1:
- In the Windows login screen click the Power button
- While holding the Shift button click Restart
- Choose Troubleshoot
- Go to the Advanced Options and then to Startup Settings
- In Startup Settings choose Enable Safe Mode
For Windows 10:
- In the Windows login screen click the Power button
- While holding the Shift button click Restart
- Choose Troubleshoot
- Go to the Advanced Options and then to Startup Settings
- In Startup Settings choose Enable Safe Mode
After the system loads you may try to uninstall the program once again or to remove its files and folders.
Method 4
If the application has been installed recently, then you may try to restore your system condition to the date before the installation.
- Open Control Panel
- Change the view to Small icons
- Click System
- Choose System Protection
- Click the System Restore… button
- Follow the on-screen instructions
Method 5
Since some of malware use a disguise of a browser add-on, you will need to check the list of extensions/add-ons in your browser.
How to remove malware from Google Chrome
- Start Google Chrome
- Click on More tools, then go to the Extensions
- Delete malware or other extensions that look suspicious and you don’t remember installing them
How to remove malware from Internet Explorer
- Launch Internet Explorer
- Click on the Tools/Gear icon, then select Manage Add-ons
- Delete malware or other extensions that look suspicious and you don’t remember installing them
How to remove malware from Mozilla Firefox
- Start Mozilla Firefox
- Click on the right-upper corner button
- Click Add-ons, then go to Extensions
- Delete malware or other extensions that look suspicious and you don’t remember installing them
How to remove malware from Microsoft Edge
- Start Microsoft Edge
- Click the three-dot button in the upper right corner
- Choose Extensions
- Click the gear icon near malware or other extensions that look suspicious and you don’t remember installing them
- Choose Remove
Method 6
Reset your browsers
How to reset settings in Google Chrome
- Click on the icon in the right-upper corner
- Choose Settings
- Click Advanced settings
- Click the Reset button
- In “reset” window click the Reset button
How to reset settings in Mozilla Firefox
- Click the icon in the upper right corner
- Choose Help
- Select Troubleshooting Information
- Click the Refresh Firefox… button
How to reset settings in Internet Explorer
- Click on the Tools button
- Go to Internet options
- Go to the Advanced tab
- Click Reset
How to reset settings in Microsoft Edge
- Start Microsoft Edge
- Click the three-dot button in the upper right corner
- Choose Settings
- Under the Clear browsing data category select Choose what to clear
- Select everything and click Clear
Method 7
Checking “hosts” file
Some viruses replace “hosts” file, writing in its version of the file strings that change your connection to the sites. As a result, when opening a popular site, you get to the scam site, made by analogy. This deceptive technique is called “phishing”. Cybercriminals use it to steal your personal data like passwords, bank information and so on.
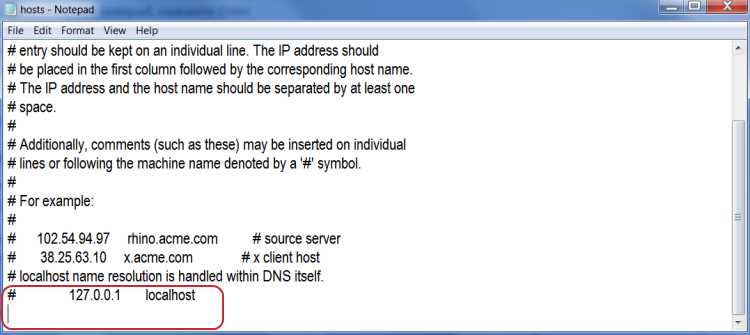
- Go to C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
- Select and open “hosts” file via Notepad.
- Delete all entries below line 127.0.0.1. Be sure to scroll the entire file down to make sure that nothing is written below this line.
- Save and close file
Method 8
Check browser shortcuts
If your browser goes to suspicious sites after you launch it, and the antiviruses “say” that everything is ok – perhaps a malicious command was added to the browser shortcut. To check the shortcut, go to its properties (the screenshot below shows the google chrome browser shortcut).
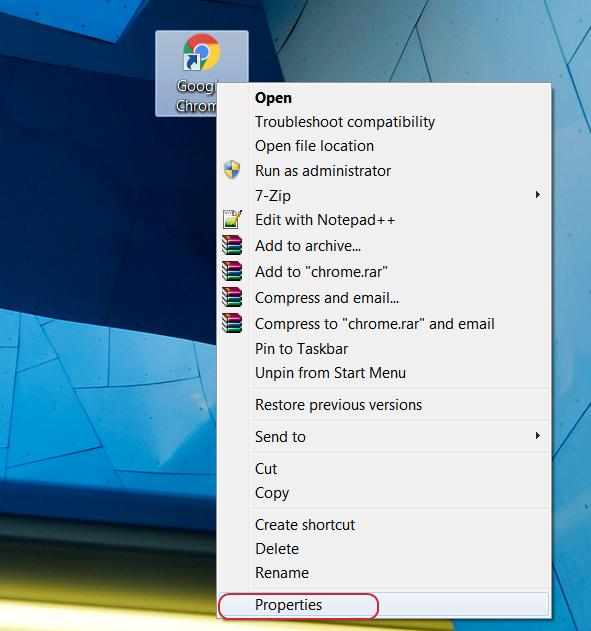
Next, look at the full launch line – “Target” or “Object”. The screenshot below shows the line as it should look if everything is ok.
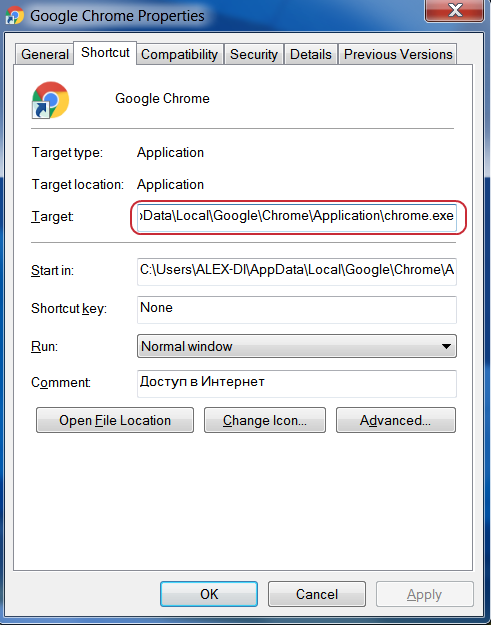
Method 9
Clean the Windows registry from viruses
Cleaning the registry must be done in normal (not safe) mode. To get started, go to the registry editor:
- Press Win + R, enter Regedit and press Enter.
- Viruses and unwanted programs create entries in the registry to download or update their files when Windows loads. These entries are located in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE and HKEY_CURRENT_USER registry keys along the path /Software/Microsoft/Windows/Current Version in the Run and RunOnce folders. If these branches (Run and RunOnce) have registry entries that are responsible for malicious processes, delete them. To do this, right-click on the desired file and click Delete.
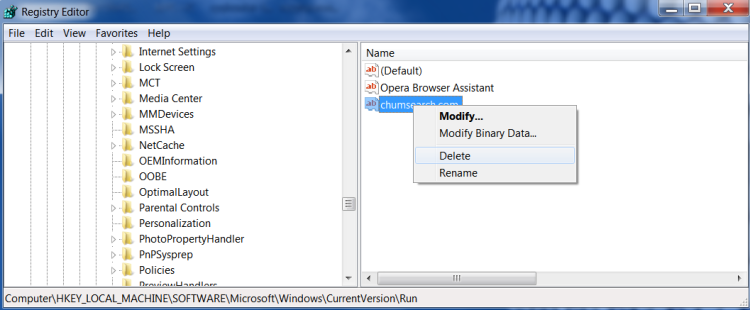
- After that, search for the names of malicious processes in the registry. In the Registry Editor, select Computer, and on the Edit tab, click Find. Enter the names of the malicious processes that you recorded and click on Find Next. Delete all found registry entries in which these processes occur. To do this, right-click on the file and click Delete. After each deletion, press the F3 key (re-search for malicious registry entries with the specified name). This action should be repeated until the registry editor detects any malicious entries for your search query. Be very careful, if you delete the system branch in the registry editor, the computer will stop working. After deleting all entries, close the registry editor.
If the above-mentioned methods didn’t help in eliminating the threat, then it’s better to rely on an automatic way of deleting malware.
We also recommend to download and use Norton to scan the system after malware removal to make sure that it is completely gone. The antimalware application will detect any vicious components left among system files and registry entries that can recover malware.